Overview
While Godot's built-in editor is quite powerful, integrating external editors like VSCode or Cursor can further improve development efficiency. This article explains setup procedures through practical best practices.
Why Use an External Editor?
External editor integration offers these specific benefits:
-
Intelligent Coding Assistance: Installing Godot extensions (Language Server Protocol) in VSCode provides advanced code completion, go-to-definition, and error checking. Combining with Cursor or GitHub Copilot enables AI code generation.
-
Rich Extension Ecosystem: Leverage countless development-helpful extensions like Git integration (GitLens), database management, and API clients.
-
Customization and Advanced Editing Features: Bring your familiar editing environment to Godot development—multi-cursor, advanced search & replace, snippet registration, Vim/Emacs keybindings, and more.
Setup Procedure
Step 1: Godot Configuration
- Open
Editor→Editor Settingsfrom Godot's menu bar. - Select
Text Editor→Externalin the left panel. - Check
Use External Editor.
-
Specify the full path to your editor's executable in
Exec Path.- VSCode (Windows):
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Programs\Microsoft VS Code\Code.exe - VSCode (macOS):
/Applications/Visual Studio Code.app/Contents/Resources/app/bin/code - Cursor (Windows):
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Programs\Cursor\Cursor.exe - Cursor (macOS):
/Applications/Cursor.app/Contents/MacOS/Cursor
- VSCode (Windows):
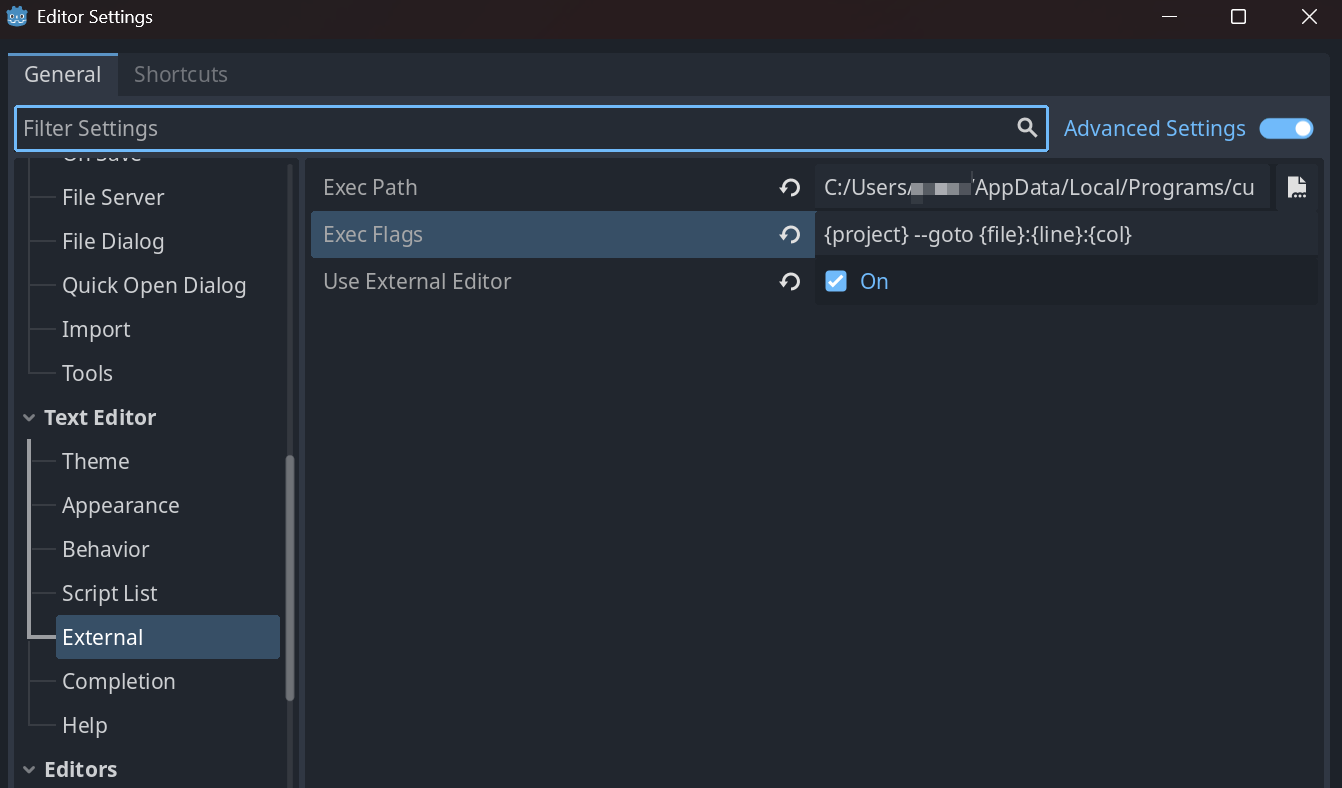
-
Set the following string in
Exec Flags.{project} --goto {file}:{line}:{col}
Step 2: Install Godot Extension in VSCode
- Open VSCode and go to the Extensions view (
Ctrl+Shift+X). - Search for
Godot Toolsand install the extension officially provided by the Godot Engine team. - After installation, if the Godot version appears in the bottom left of VSCode, integration is ready.
Step 3: Debug and Auto-Reload Settings
Debug Integration: Check "Debug with External Editor" in the script editor's "Debug" menu. When errors occur, the relevant location opens in the external editor.

Auto Reload: Enable "Editor Settings" → "Text Editor" → "Behavior" → "Auto Reload Scripts on External Change". Saves in the external editor are immediately reflected in Godot.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
| Common Mistake | Best Practice | |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | Specifying a shortcut path in Exec Path | Always specify the full path to the executable file (.exe or binary) |
| Workflow | Manually switching between Godot and VSCode after each change | Enable Auto Reload so saves in VSCode are automatically reflected in Godot |
| Debugging | Relying entirely on print() debugging | Use Godot Tools' debugging features. Set breakpoints and step through while inspecting variable contents |
| Code Management | Not using Git for the project folder | Use Git version control from the start to leverage VSCode's powerful Git integration (GitLens, etc.) |
Troubleshooting
| Symptom | Check Points |
|---|---|
| Files don't open | Verify Exec Path and flags syntax |
| Changes aren't reflected | Enable Auto Reload Scripts on External Change |
| Internal editor opens during debug | Enable Debug with External Editor |
Choosing Between Built-in and External Editor
| Built-in Editor | External Editor (VSCode) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Quick to launch and convenient, excellent for shader editing | Advanced code completion, rich extensions, powerful debugging and Git integration |
| Cons | Limited code completion, lacks refactoring features | Requires initial setup, needs separate launch/management |
| Recommended For | Small prototyping, shader fine-tuning | Medium to large projects, team development |
Summary
External editor integration becomes a powerful weapon in Godot development. Build a comfortable development environment by leveraging the powerful features of VSCode or Cursor.